Graduate vs Undergraduate
When comparing undergraduate vs graduate education, the differences extend beyond just the sequence of degrees. These distinct educational paths serve different purposes and offer varying benefits.
The financial impact of graduate education is substantial. Master’s degree holders earn median weekly earnings of $1,574 compared to $1,334 for bachelor’s degree holders. This jumps even higher to $1,909 weekly for those with doctoral degrees. Over a lifetime, men with graduate degrees earn $1.5 million more than high school graduates, while women with graduate degrees earn $1.1 million more.
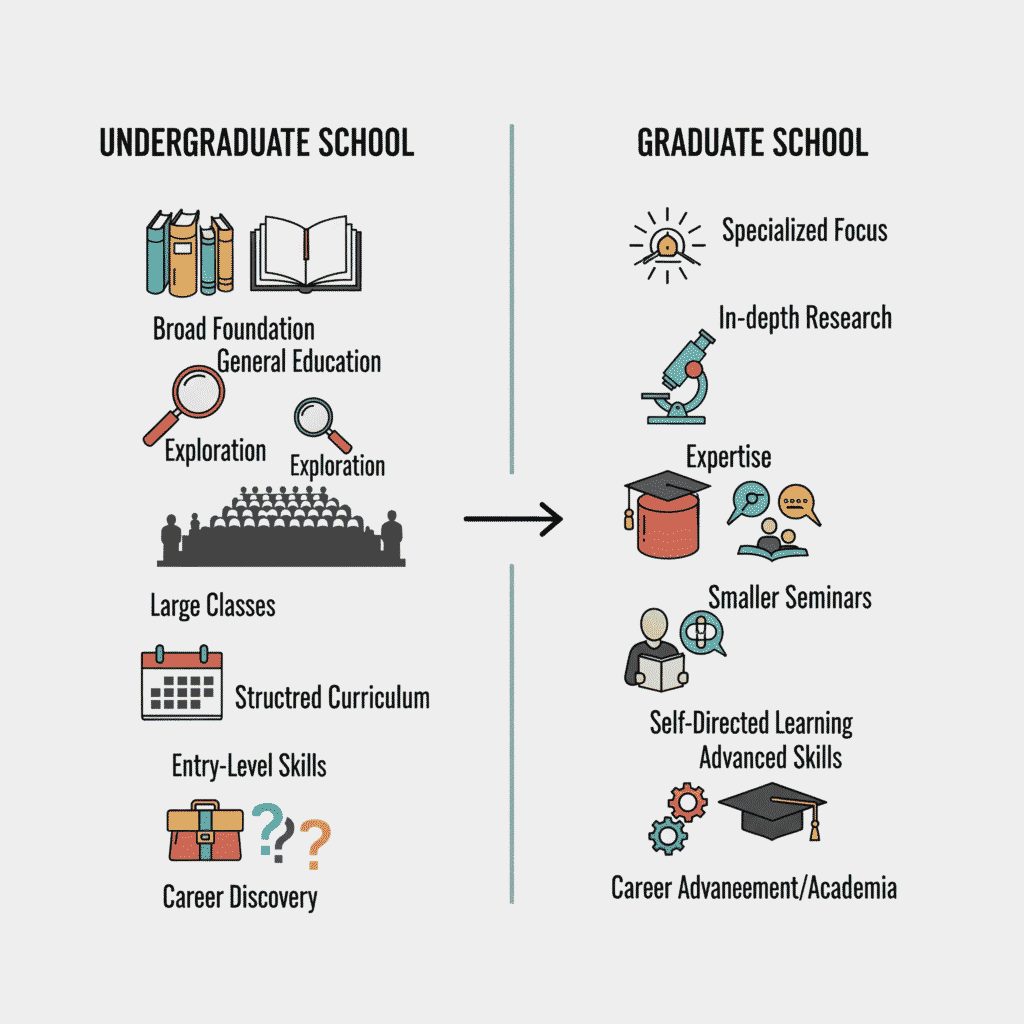
Graduate programs differ markedly in their educational approach. Undergraduate students typically juggle 5-6 courses per semester across diverse subjects, whereas graduate students take approximately 3 advanced-level courses focused specifically on their field. Moreover, graduate coursework involves significantly more reading, research, and independent work.
The classroom dynamic also shifts considerably. Undergraduate lectures often accommodate hundreds of students, but graduate classes typically function as intimate seminars with fewer than 20 students. Notably, professors in graduate settings often treat students more as peers than subordinates.
Community demographics vary between these educational levels. Undergraduate students are typically in their early twenties, whereas graduate students are often in their late twenties or early thirties, balancing studies with work and family responsibilities. Indeed, the average age for a graduate student is 33, with most working at least part-time.
Graduate education primarily focuses on specialization, transforming students from generalists to experts. Undergraduate programs provide foundational knowledge across various subjects, whereas graduate studies develop advanced expertise in specific disciplines. This specialization often leads to greater professional marketability, with graduates seeing 57% more job opportunities than non-graduates.
Ultimately, the choice between concluding education at the undergraduate level or pursuing graduate studies depends on career goals, financial considerations, and personal circumstances within your chosen field.
Undergraduate Mean
Understanding undergraduate education helps clarify the fundamental differences between undergraduate and graduate studies. The term “undergraduate” refers to postsecondary education that leads to a bachelor’s or associate degree, forming the foundation of higher education for most students.
Degree Structure and Time Periods
The undergraduate program is specially begin after high school (12th grade) completed. Undergraduates degree is also known as Bachelor Degree. This degree is typically four year of full time study. Most bachelor’s programs follow a structured curriculum that includes:
- General education requirements covering diverse subjects like mathematics, sciences, humanities, and communication
- Major-specific courses that provide in-depth knowledge in the chosen field of study
- Elective courses allowing students to explore additional interests
- Possibly minor areas of study, internships, or capstone projects
Academic Considerations
The undergraduate program focus on huge knowledge in particular course. The program schedule as a semester wise or quarter system wise with define class time and attendance requirements.
Career after Undergraduate
A bachelor’s degree serves as the minimum qualification for many entry-level professional positions across various industries. Some careers specifically require undergraduate degrees in relevant fields. Many graduates enter the employees immediately after completing their undergraduate studies, while others choose to pursue advanced degrees. The undergraduate experience provides valuable skills applicable to diverse career paths, including critical thinking, communication, and subject-specific knowledge that employers value.
Graduate Mean
Graduate education represents a significant step beyond undergraduate studies, offering specialized knowledge and advanced skills in specific disciplines. Unlike the broader undergraduate experience, graduate programs narrow their focus considerably.
Degree Structure and Time Periods
Master’s degrees typically require 1.5 to 2 years of full-time study to complete. Most programs demand between 30 to 60 credit hours, with some requiring as many as 72 credits. Program completion times vary based on several factors:
- Full-time students may finish some 34-credit programs in as little as 12 months
- Part-time enrollment extends completion timelines, sometimes taking up to three years
- Online programs often provide more flexibility in scheduling and pacing
Many graduate programs join thesis requirements, capstone projects, or internships as culminating experiences. These components demonstrate mastery of the field and application of advanced knowledge. Furthermore, accelerated master’s programs allow students to earn dual course credit, potentially shortening degree completion time by an entire academic year.
Financial and Cost
Graduate education represents a substantial financial investment. The average total cost of graduate school is approximately $43,620 per year. This varies significantly by program type:
- Master’s degrees average $36,760 annually ($73,520 for two years)
- Private, nonprofit institutions cost the most, with private for-profit schools costing over $20,000 less
- Online master’s programs typically cost 45% less than in-person options
Consequently, many students graduate with significant debt. Master’s degree holders carry an average of $46,798 in student loan debt, which is 23% more than bachelor’s degree holders.
Career after Graduate
The career impact of graduate education is substantial. According to BLS data, master’s degree holders earn a median weekly salary of $1,737 compared to $1,493 for those with bachelor’s degrees. This represents a 20% earnings premium over bachelor’s degree holders.
In addition to higher salaries, graduate degrees often lead to:
- Lower unemployment rates compared to those with only bachelor’s degrees
- Increased job security and stability in many fields
- Greater opportunities for specialized roles and leadership positions
Graduate degrees have become increasingly important in certain fields. In fact, 33% of organizations now hire employees with master’s degrees for positions previously held by those with only bachelor’s degrees. Most importantly, specialized graduate education provides in-depth knowledge that can significantly enhance career prospects and professional growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Undergraduate |
| Program Duration | 4 years (Bachelor’s) 2 years (Associate’s) |
| Class Size | Hundreds of students in lectures |
| Course Load | 5-6 courses per semester |
| Academic Focus | Broad knowledge across multiple subjects |
| Teaching Format | Lecture-style, structured classes |
| Student Age | Early twenties |
| Employment Status | Typically full-time students |
| Weekly Earnings (Post-graduation) | $1,334 |
| Aspect | |
| Student Life | Campus-based, emphasis on activities and social events |
| Student-Professor Dynamic | Traditional teacher-student relationship |
[…] Top Reasons to Study in France: A Smart Choice for International Students […]
[…] Admission Requirements for Study in France: Complete Guide […]
[…] Also Read: Eiffel Excellence Scholarship Program (2026) […]
[…] 500 French words with meaning for International Student […]
[…] Complete Guide to Study in France Requirements from Nepal […]
- How to Write an SOP for a French Scholarship or University Application
- The Climate and Weather in France: What Students Should Know
- Top French Universities and Schools for International Students
- How to Find Work in France as an International Student
- Undergraduate Scholarships in France for International Students

2 thoughts on “Undergraduate vs Graduate School: Cost, Time & Career Impact”